 *Bones of the gluteal region
*Bones of the gluteal region
Outer(external) surface of hip bone
sacrum
coccyx
upper part(half) of the femur
*Layers of gluteal region
1) skin * thick
* With large amount of sweat gland and hair of follicles
2) superficial fascia ((contain large amount of fat that increase the mass of the region &contain superficial vessels and nerves ))
3) deep fascia
4) muscles
*Skin of gluteal region is divided into 4-quarters
upper lateral
upper medial
lower lateral
lower medial
§ N.B §
( the common site of intramuscular injection (IM) is in the upper lateral quarter which is called the safest area for I.M injection )
Which can be marked by rule of Thumb ≈ by putting the thumb on ASIS
& the tip of the index is pointing toward the site of injection
Below this area there are minimal number of vessels & nerves
[The Muscles]
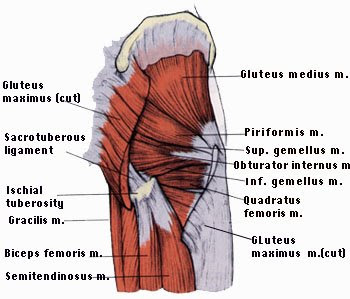
Gluteus maximus
Largest muscle in the body
It forms most of the mass of gluteal region
O : outer surface of ilium & sacrum & coccyx
INS : 1) upper quarter to linea aspra
2) lower 3 quarters to iliotibial tract
● N .S : inferior gluteal nerve branch from sacral plexus
● Action : 1) extention of the hip
2) lateral rotation of the hip
Gluteus medius
▲ in shape
Below(deep to) maximus
Above(superficial to) minimus
O : outer surface of ilium
Ins : greater trochanter of femur
N .S : superior gluteal nerve
Action : steady the pelvis while walking or when you left your foot of the ground by ABDUCTION of the hip ( other side hip )
Gluteus minimus
▲in shape
Below medius
O: outer surface of ilium
Ins : greater trochanter of femur
N.S : superior gluteal nerve
Action : same as medius BECAUSE both cooperate to perform common action to steady the pelvis
N.B : if the superior gluteal nerve is cut the result will be paralysis of medius & minimus leading to Tilting of the pelvis while walking called Duck Gaite
Piriformis
Pear- shaped
O: anterior surface of sacrum in site pelvis then leave through greater sciatic foramen to reach gluteal region
Ins : greater trochanter of femur
N.S : sacral plexus
Action : lateral rotation
N.B : -ALL Structure pass superior to piriformis are called superior ( gluteal V&A&N)
-Most structure pass below piriformis are called inferior gluteal V&A& N)
●N.B: Piriformis is the key identification of the structure in Gluteal region to mark or identify structure .

Obturator internus
Fan- shaped
O: inner margin of obturator foramen inside the pelvis then leave through lesser sciatic foramen
Ins: greater trochanter of femur
N.S : nerve to obturator internus from sacral plexus
Action : lateral rotation

Gemellus superior
O : spine of ischium
Ins : greater trochanter with obturator internus
N.S: nerve to obturator internus
Action : lateral rotation
Gemellus inferior
O: ischial tuberosity
Ins: greater trochanter
N.S: Nerve to quadratus femoris
Action : lateral rotation
Quadratus femoris
Quadrangular in shape
O: ischial tuerosity
Ins: intertrochanteric crest
N.S: nerve to quadratus femoris
Action : lateral rotation of femur
N.B : IF THE NECK OF FEMUR IS FRACTURED . THE PATIENT AT BED HIS FOOT WILL BE LATERAL IN ROTATED SO WE MUST tie the 2 thumb together>> to protect sciatic nerve because if fractured occure then the greater trochanter will close to ischial tuberosity so it may be cut the sciatic nerve which is located between them .






No comments:
Post a Comment